Hue has just blown its 10th candle! In this follow-up #2 of the series, let's describe what a SQL Cloud Editor is.
The top two capabilities of a SQL Cloud Editor are:
Data Querying Experience: offer a SQL querying assistant that helps users self service their own query need while educating them on the data and syntax know-how.Cloud Native: scale by providing as much as “no-ops” as possible by automating the operation of the service. Easy to run and monitor, auto scale in capacity, automatic rolling upgrades…
This post is about detailing the Querying Experience from the point of a end user. #3 post of the series will focus on the Cloud Experience.
Focus on SQL Data Warehousing
Many Data Platforms are typically configured in a Data Hub model. This means a centralized cluster with all the data, computes and satellite services like workflow scheduling, indexing, streams… altogether.
This is a lot of components to access via a full blown Hue:
Hue's apps range from Dashboards for light calculation or charting of indexed or SQL data, browser for the Cloud storages of AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, scheduling workflows of jobs, a dataset importer wizard…
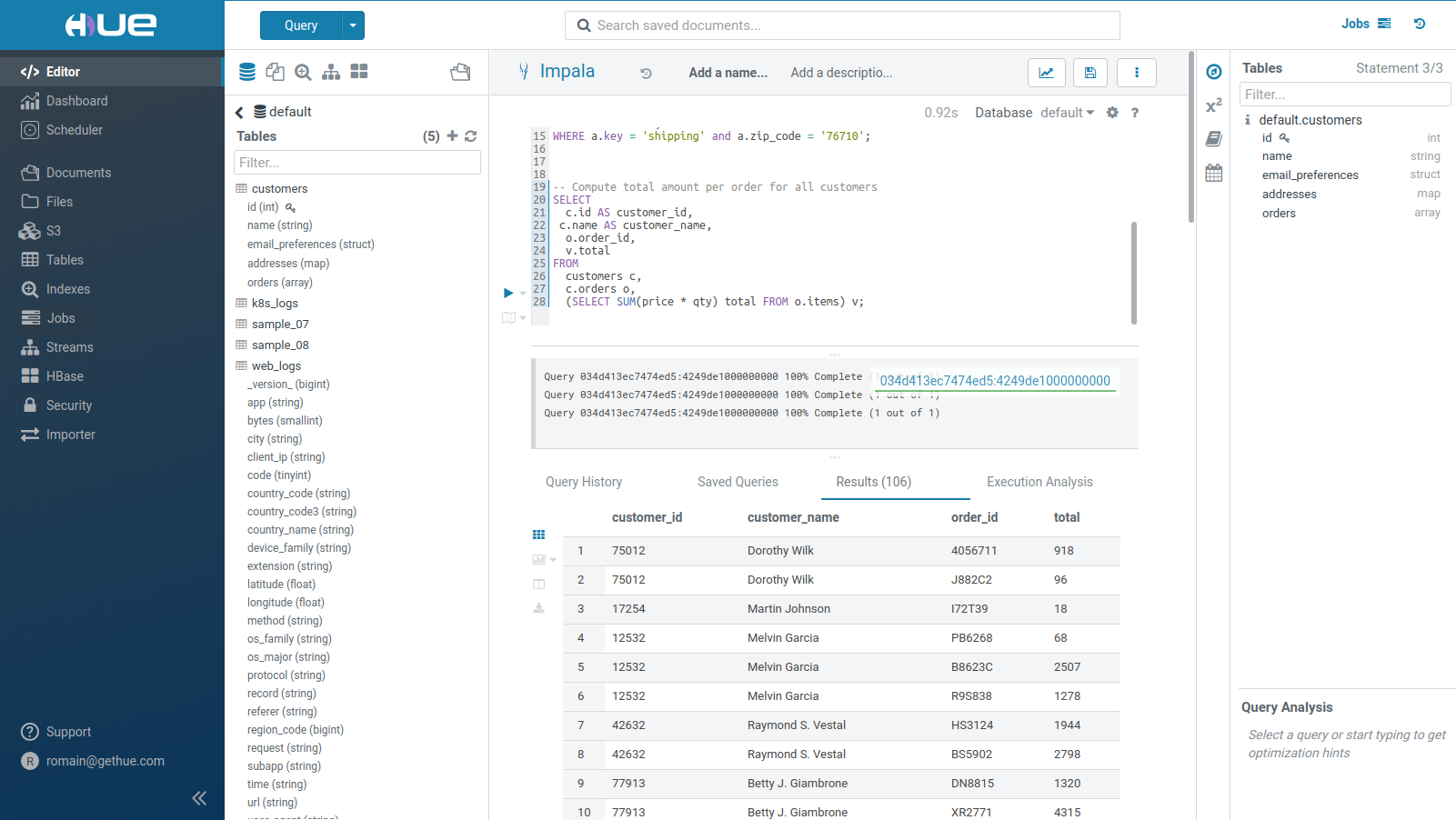
However in the case of SQL Data Warehousing, we want to restrict Hue to mostly the Editor and Data Catalog:
That way, the SQL Compute Engines and Data Storages can be easily queried or browsed.
SQL Querying Experience
Querying Data is hard. It is not simple to have the knowledge of the existing datasets and how to query them. Traditional SQL Editors targeted advanced and full time users like SQL Developers of Data Analysts and provided interfaces filled-up with options.
Now the modern trend is to provide the simplest interface to a wider range of end users and basically hide under the cover a maximum of the complexity of the big data ecosystem. Typically, non full time Data Analysts don't even know how to get started, so a smart editor should crowdsource the data descriptions as well as how to query it.
Ad-hoc queries are also a major use case, where various professions in the organization just want an answer to a basic question. e.g.
- How many clicks did we get on the blog post this week vs last week?
- What are the sales in the Japan region for product X?
- What are the top cases of our customers in Salesforce for my team?…
and it is much faster if they can answer it by themselves rather than asking for a new dashboard or SQL query to the Analytics team. What prevents them from achieving self service is often how to:
- Find the data
- Find the query
Finding the Data
Among 1000s of databases containing 10s of 1000s of tables with cryptic names, it is not an easy task. Before typing any query to get insights, users need to find and explore the correct datasets.
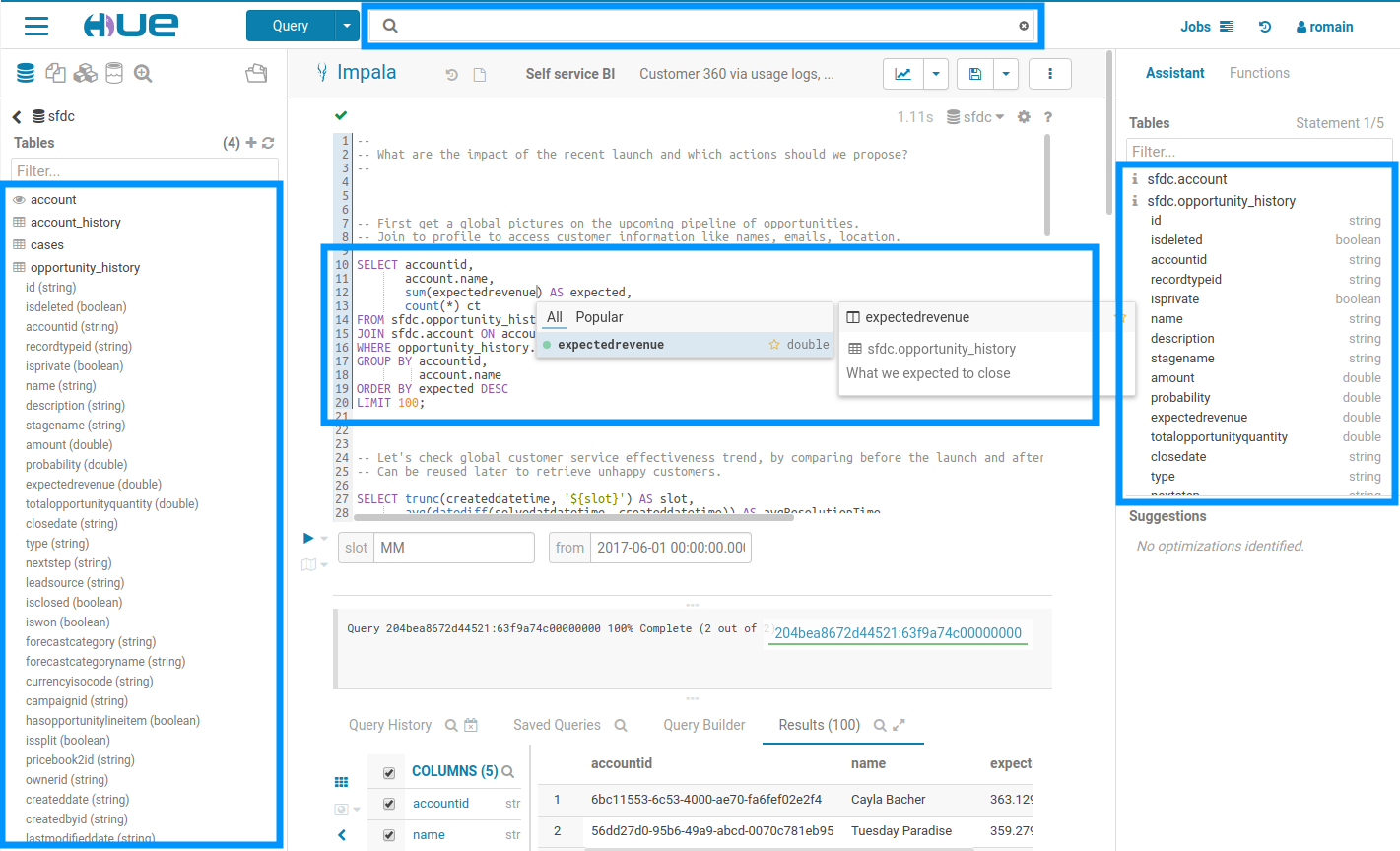
Data Browsers & Catalogs are here to help tackle this and Hue has built in integration to these services. Apache Atlas is powering the Search and Commenting of tables, columns. New Catalogs can be integrated via connectors.
Top search
Have you ever struggled to remember table names related to your project? Does it take much too long to find those columns or views? Hue lets you easily search for any table, view, or column across all databases in the cluster. With the ability to search across tens of thousands of tables, you're able to quickly find the tables that are relevant for your needs for faster data discovery.
The search bar is always accessible on the top of the screen, and it offers a document search and metadata search too if Hue is configured to access a metadata server.
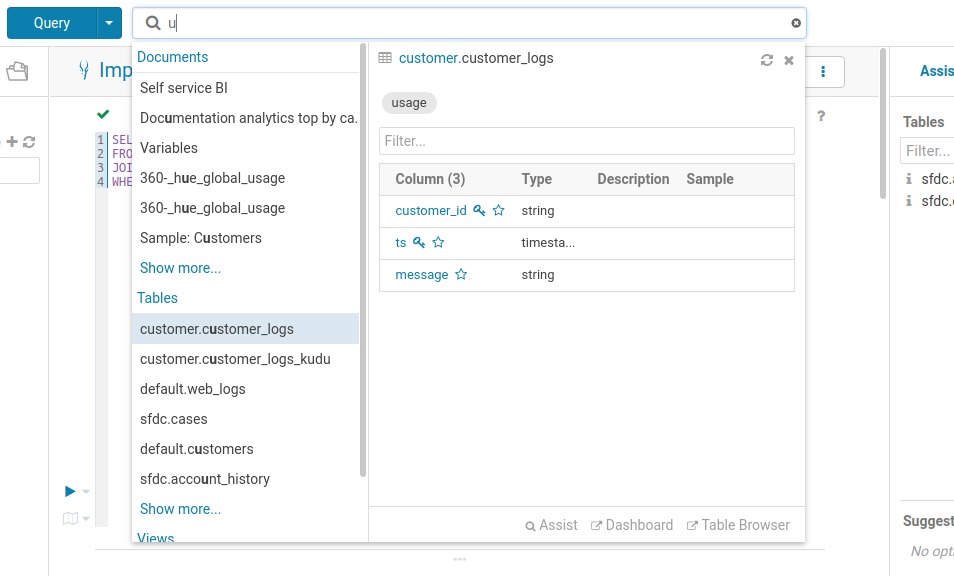
Searching all the available queries or data in the cluster
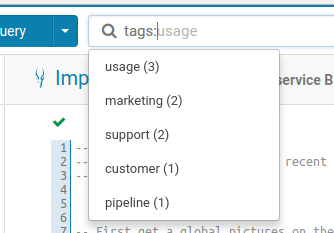
Listing the possible tags to filter on.
Search
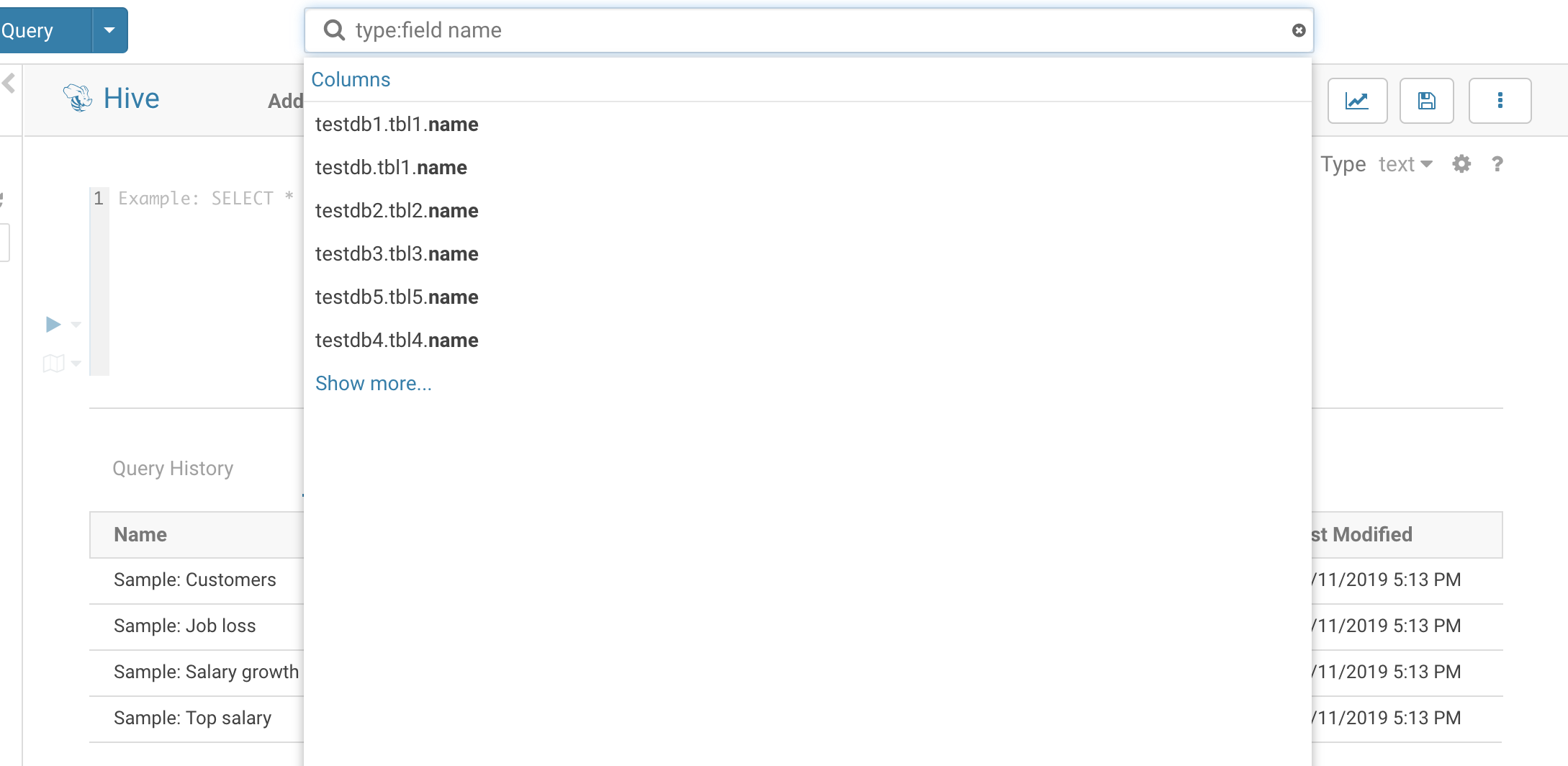
By default, only tables and views are returned. To search for columns, partitions, databases use the ‘type:’ filter.
Example of search syntax:
Apache Atlas
- sample → Any table or Hue document with prefix ‘sample’ will be returned
- type:database → List all databases on this cluster
- type:table → List all tables on this cluster
- type:field name→ List tables with field(column): ‘name’
- ‘tag:classification_testdb5‘ or ‘classification:classification_testdb5’→ List entities with classification ‘classification_testdb5’
- owner:admin→ List all tables owned by ‘admin’ user
Cloudera Navigator
- table:customer → Find the customer table
- table:tax* tags:finance → List all the tables starting with tax and tagged with ‘finance’
- owner:admin type:field usage → List all the fields created by the admin user that matches the usage string
- parentPath:"/default/web_logs” type:FIELD originalName:b* → List all the columns starting with
bof the tableweb_logsin the databasedefault.
Additional Metadata
In addition to editing the tags of any SQL objects like tables, views, columns… which has been available since version one, table descriptions can now also be edited. This allows a self service documentation of the metadata by the end users.
Left assist
Data where you need it when you need it.
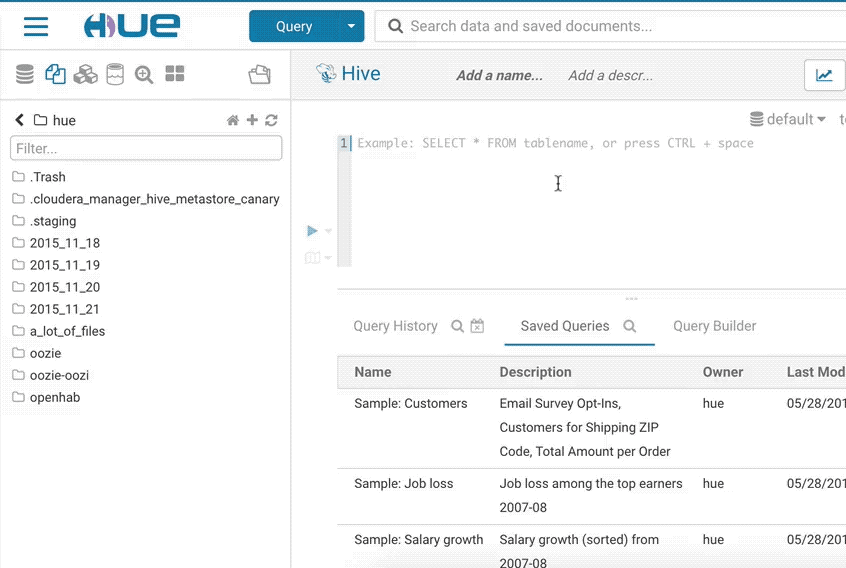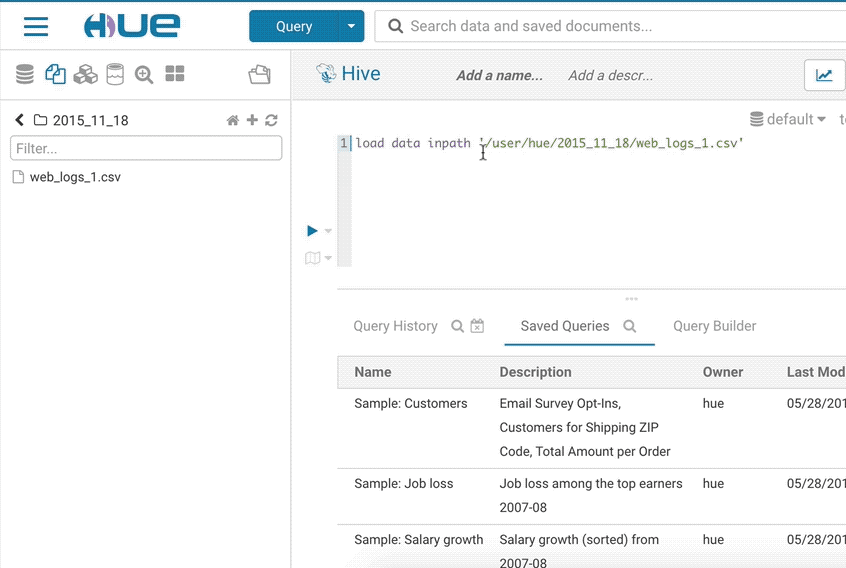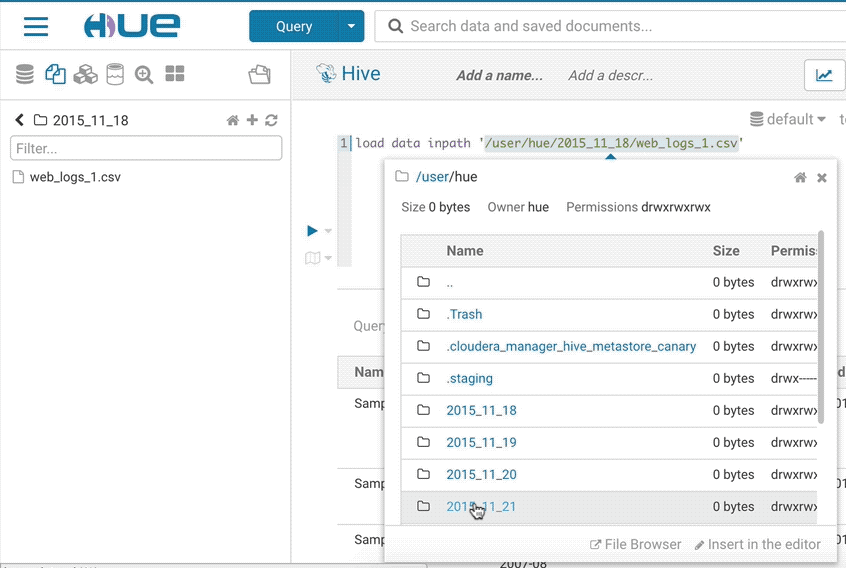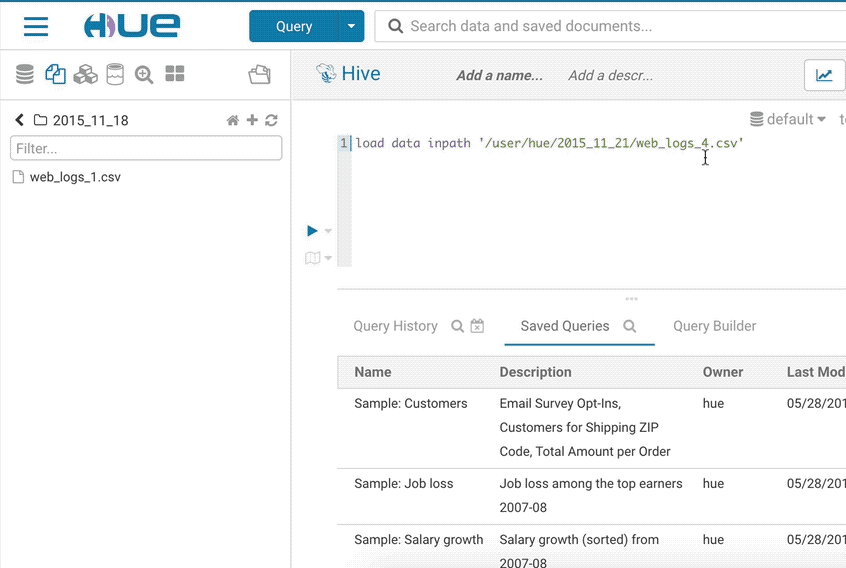
Find your queries, tables and files in the left assist panel without leaving the page. Right-clicking items will show a list of actions, you can also drag-and-drop a file to get the path in your editor and more.
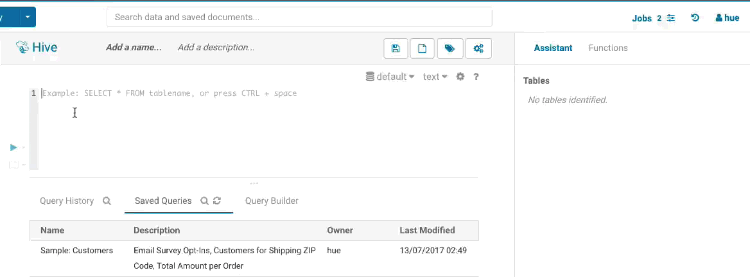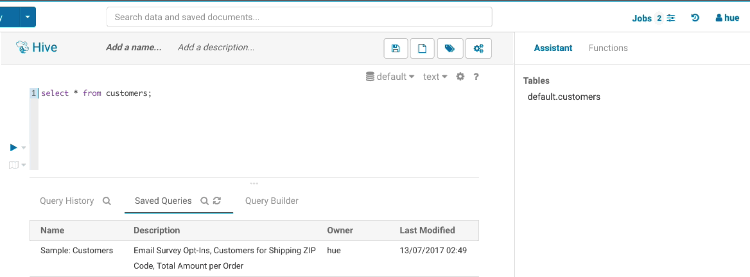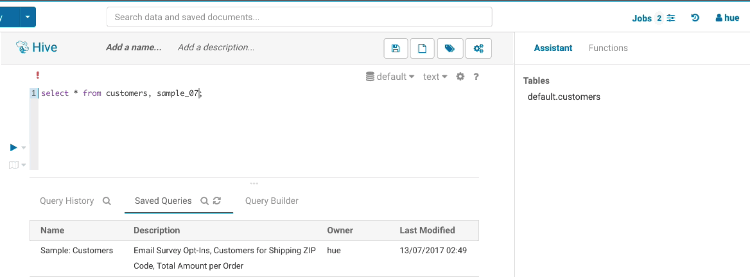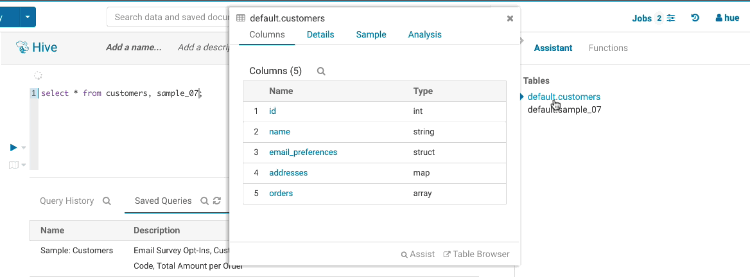
Sample popup
This popup offers a quick way to see samples of the data and other statistics on databases, tables, and columns. You can open the popup from the SQL Assist or with a right-click on any SQL object (table, column, function…). In this release, it also opens faster and caches the data.
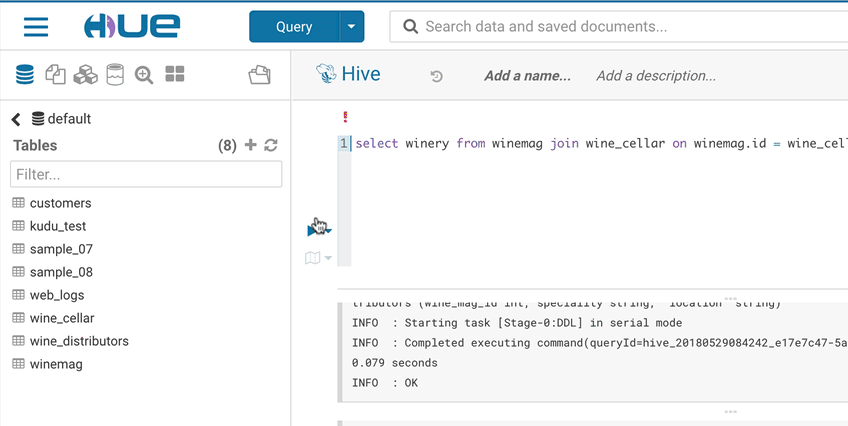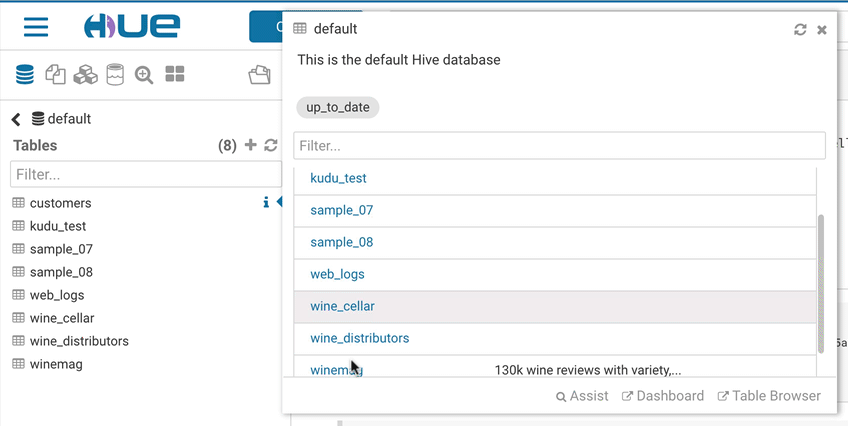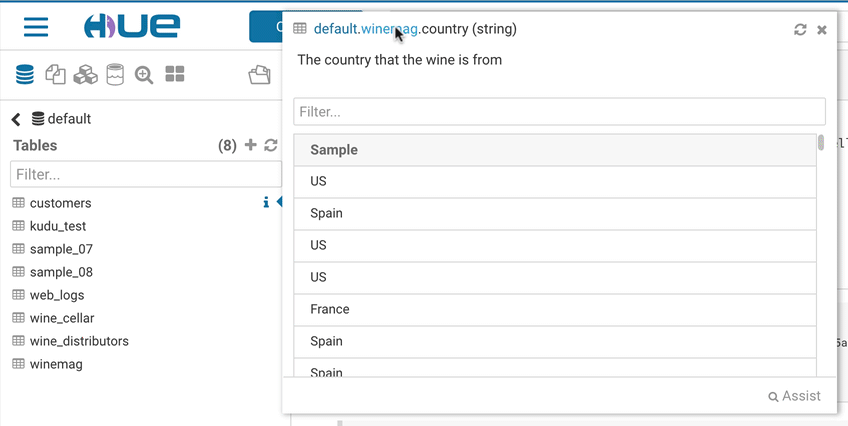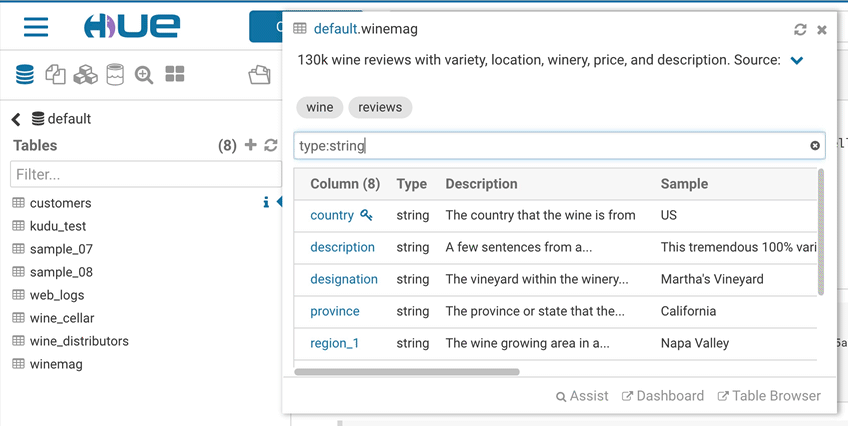
Tagging
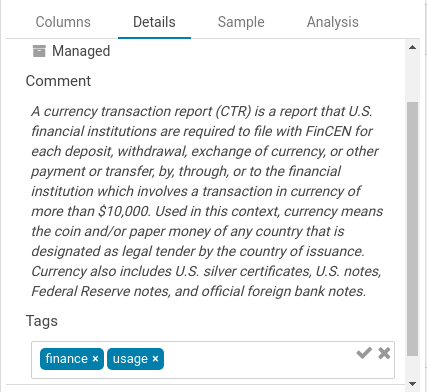
In addition, you can also now tag objects with names to better categorize them and group them to different projects. These tags are searchable, expediting the exploration process through easier, more intuitive discovery.
Browsing Data
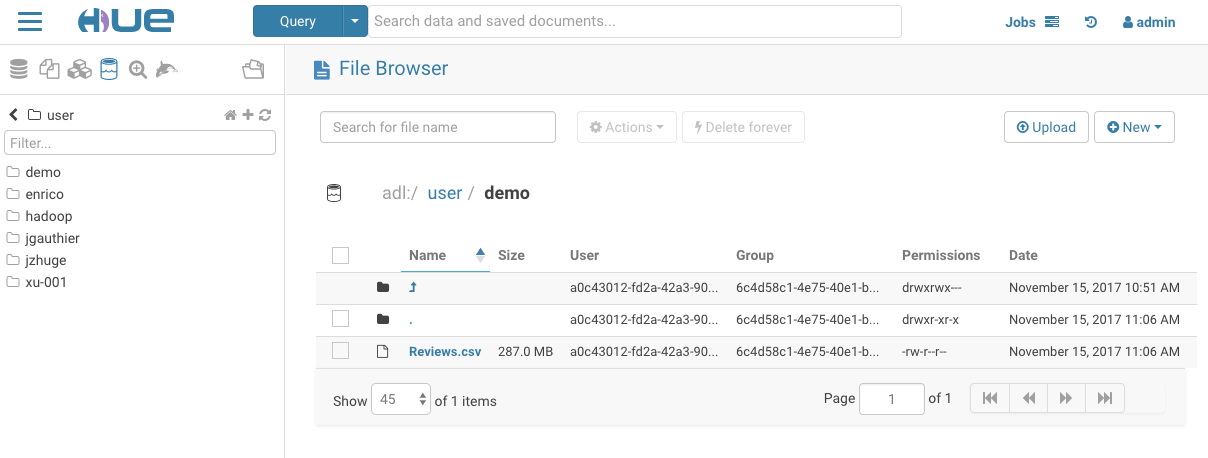
The File Browser application lets you interact with these File Systems: HDFS, AWS S3, Azure ADLS v1 and v2 (ABFS). Google Cloud Storage is currently a work in progress HUE-8978.
View all accessible folders within the account by clicking on the storage root. From here, create, rename, move, copy, or delete existing directories and files. Additionally, directly upload files to the storage.
Importing Data
The goal of the importer is to allow ad-hoc queries on data not yet in the clusters and simplifies self-service analytics.
If you want to import your own data or reference existing data not in a table, open the importer from the left menu or from the little + in the left assist. The import wizard can create external Hive tables directly from files in the storage.
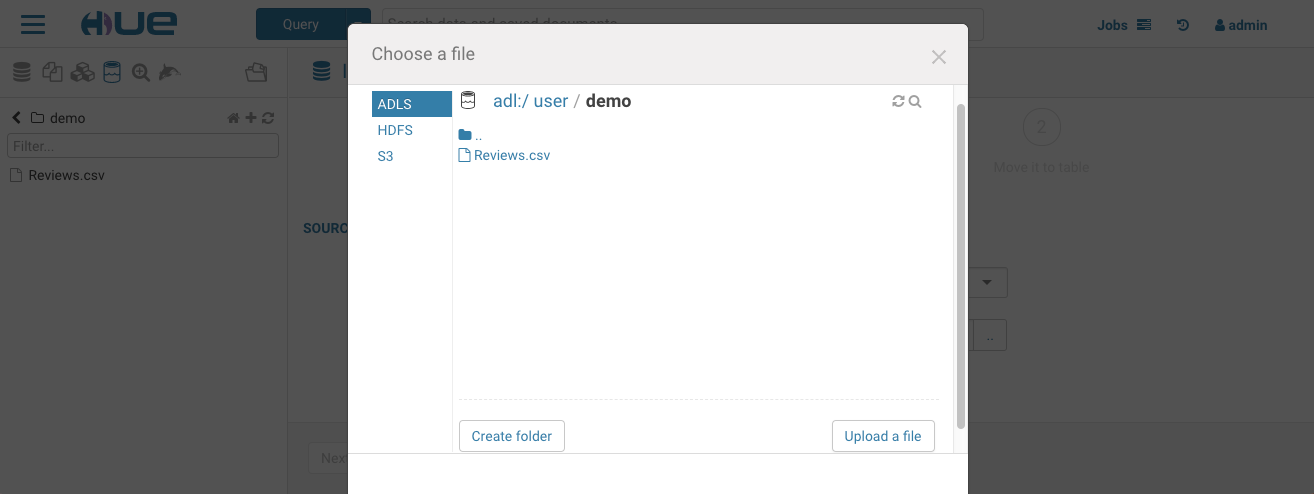
Querying the Data
Now that the tables are found, it is time to query them to answer our questions or discover insights.
Running Queries
SQL query execution is the primary use case of the Editor. See the list of most common Databases and Datawarehouses.
- The currently selected statement has a left blue border. To execute a portion of a query, highlight one or more query statements.
- Execute. Then the Query Results window appears. Perform refining operations like scroll to column, column names and types filtering, plotting, row locking/expanding, cell content search.
- If there are multiple statements in the query (separated by semicolons), click Next in the multi-statement query pane to execute the remaining statements.
When you have multiple statements it is enough to put the cursor in the statement you want to execute, the active statement is indicated with a blue gutter marking.
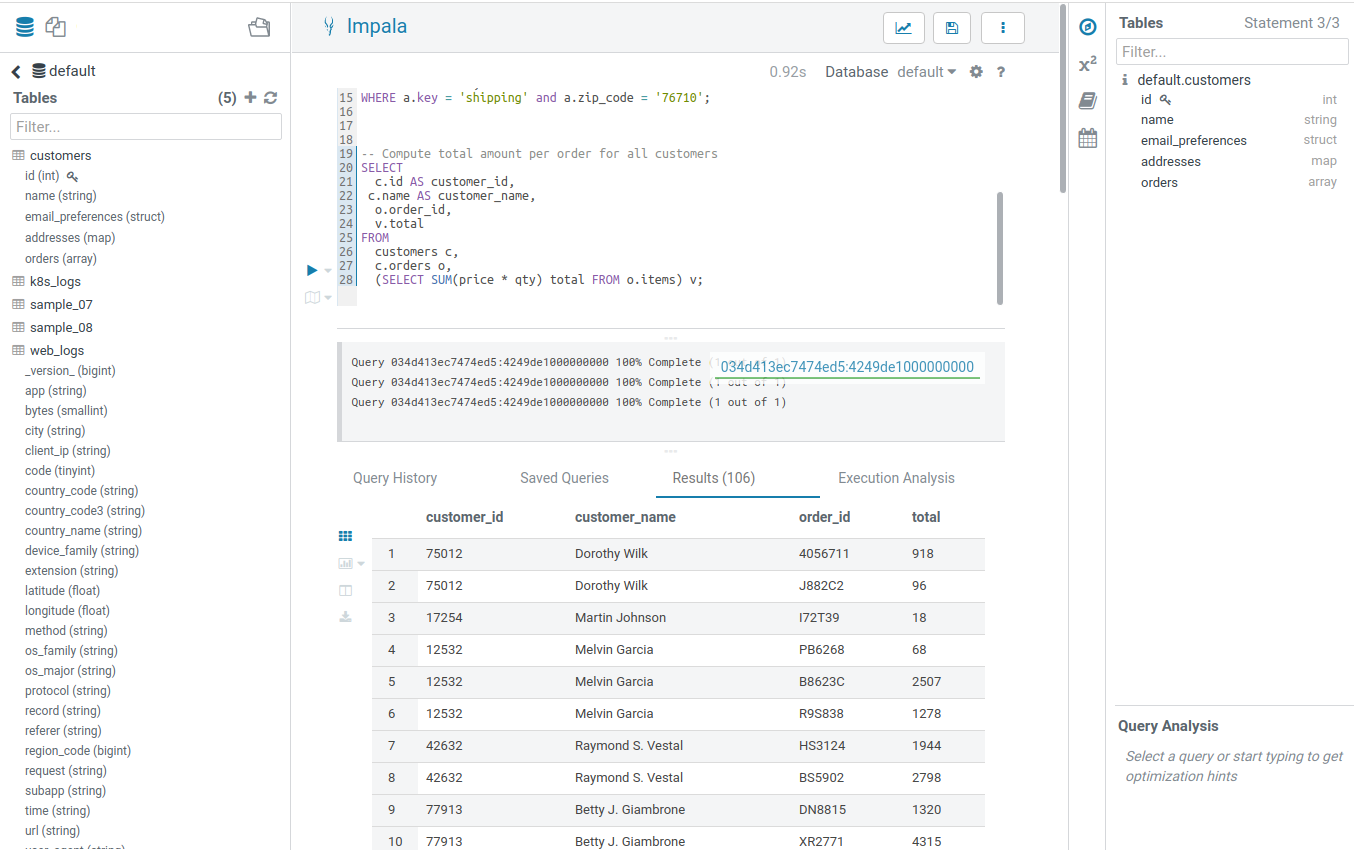
Note: Use CTRL/Cmd + ENTER to execute queries.
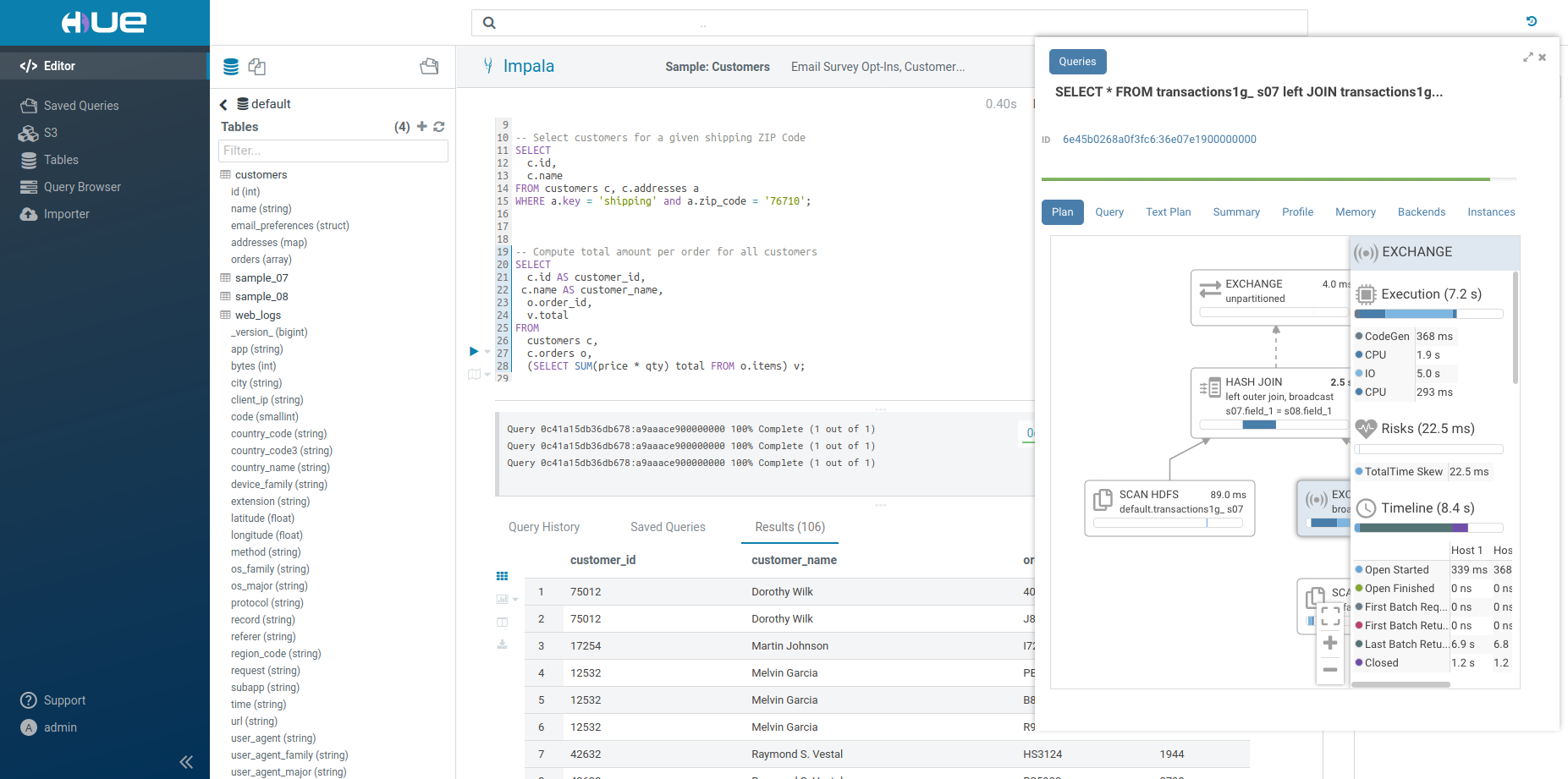
Note: On top of the logs panel, there is a link to open the query profile in the Query Browser.
Autocomplete
This is where Hue shines the best, Hue comes with one of the best SQL autocomplete on the planet. The autocompleter knows all the ins and outs of the Hive and Impala SQL dialects and will suggest keywords, functions, columns, tables, databases, etc. based on the structure of the statement and the position of the cursor.
Smart column suggestions
If multiple tables appear in the FROM clause, including derived and joined tables, it will merge the columns from all the tables and add the proper prefixes where needed. It also knows about your aliases, lateral views and complex types and will include those. It will now automatically backtick any reserved words or exotic column names where needed to prevent any mistakes.
Smart keyword completion
The autocompleter suggests keywords based on where the cursor is positioned in the statement. Where possible it will even suggest more than one word at a time, like in the case of IF NOT EXISTS, no one likes to type too much right?
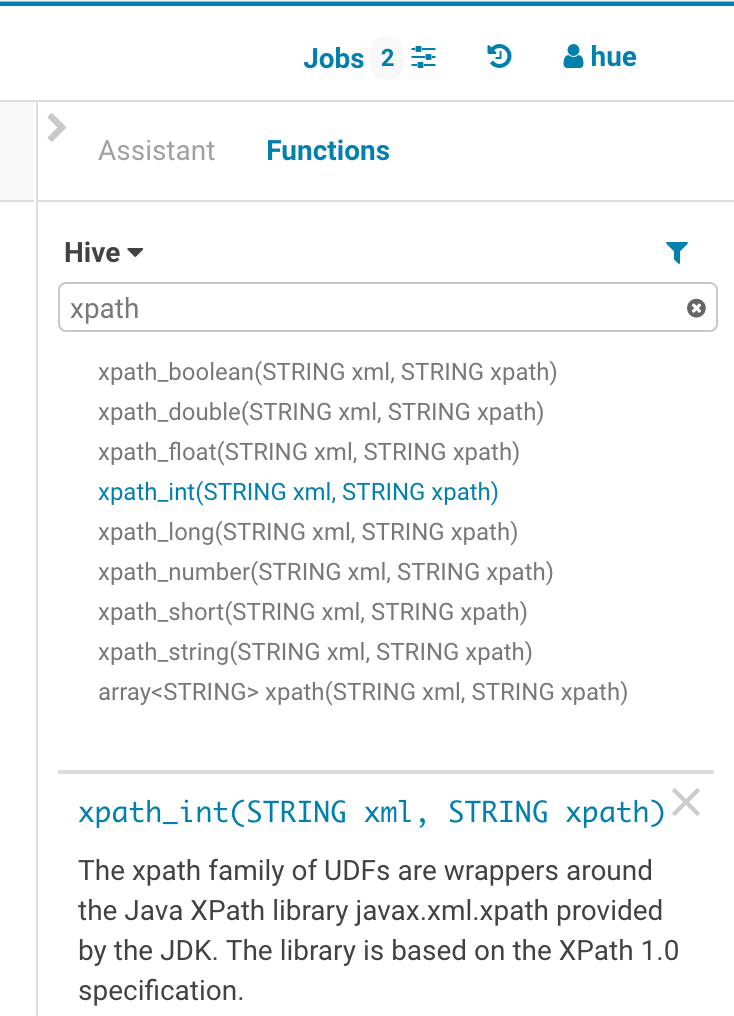
Functions
The improved autocompleter will now suggest functions, for each function suggestion an additional panel is added in the autocomplete dropdown showing the documentation and the signature of the function. The autocompleter knows about the expected types for the arguments and will only suggest the columns or functions that match the argument at the cursor position in the argument list.
Sub-queries, correlated or not
When editing subqueries it will only make suggestions within the scope of the subquery. For correlated subqueries the outside tables are also taken into account.
Context popup
Right click on any fragment of the queries (e.g. a table name) to get all its metadata information. This is a handy shortcut to get more description or check what types of values are contained in the table or columns.
It’s quite handy to be able to look at column samples while writing a query to see what type of values you can expect. Hue now has the ability to perform some operations on the sample data, you can now view distinct values as well as min and max values.
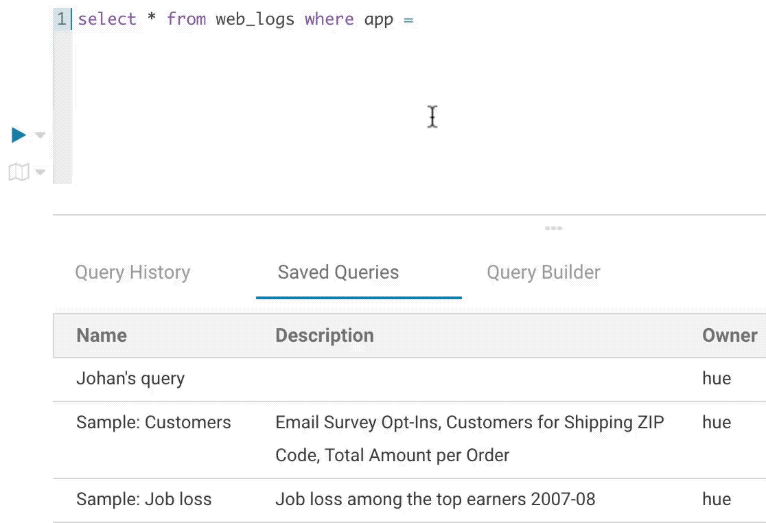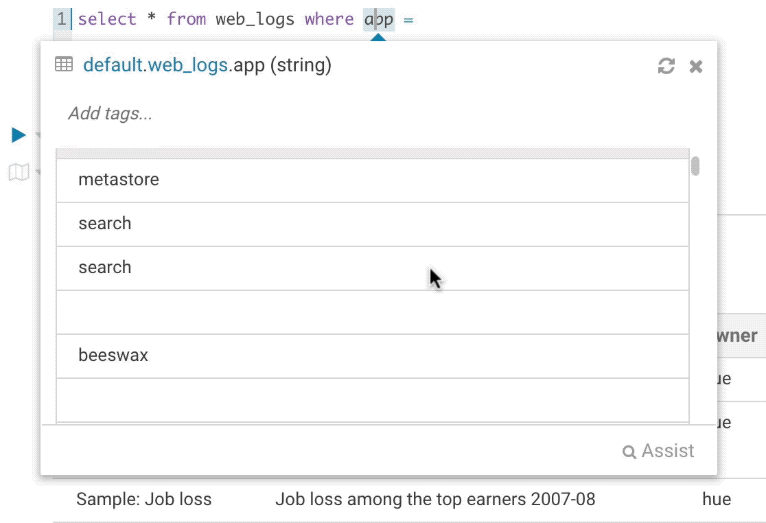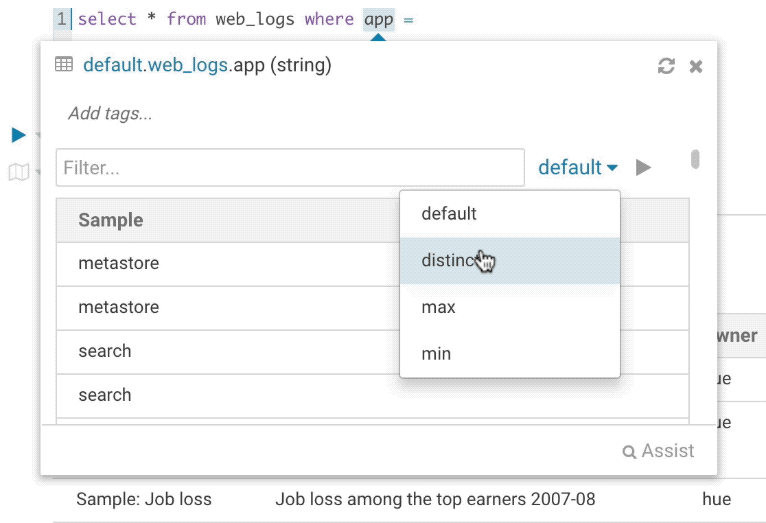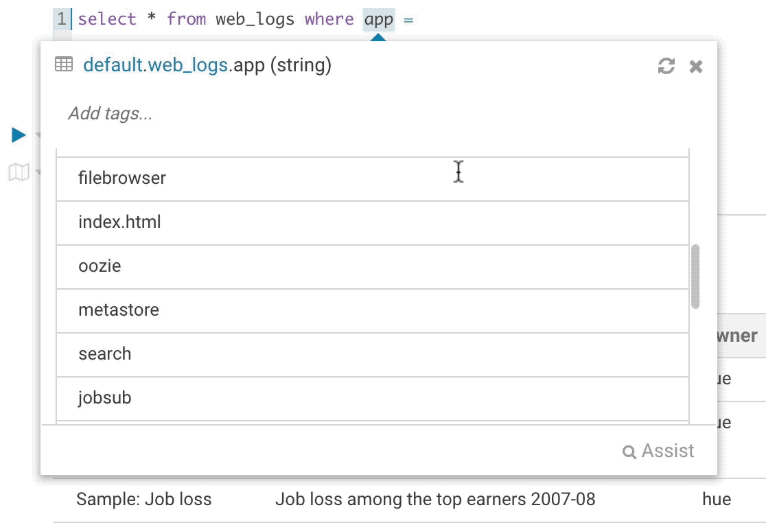
Syntax checker
A little red underline will display the incorrect syntax so that the query can be fixed before submitting. A right click offers suggestions.
Syntax checker highlight
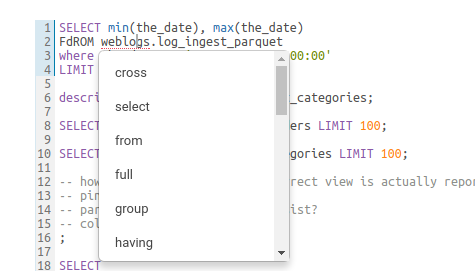
Syntax checker correction suggestion
Table Assist
The Datawarehouse ecosystem is getting more complete with the introduction of transactions. In practice, this means your tables can now support Primary Keys, INSERTs, DELETEs and UPDATEs as well as Partition Keys.
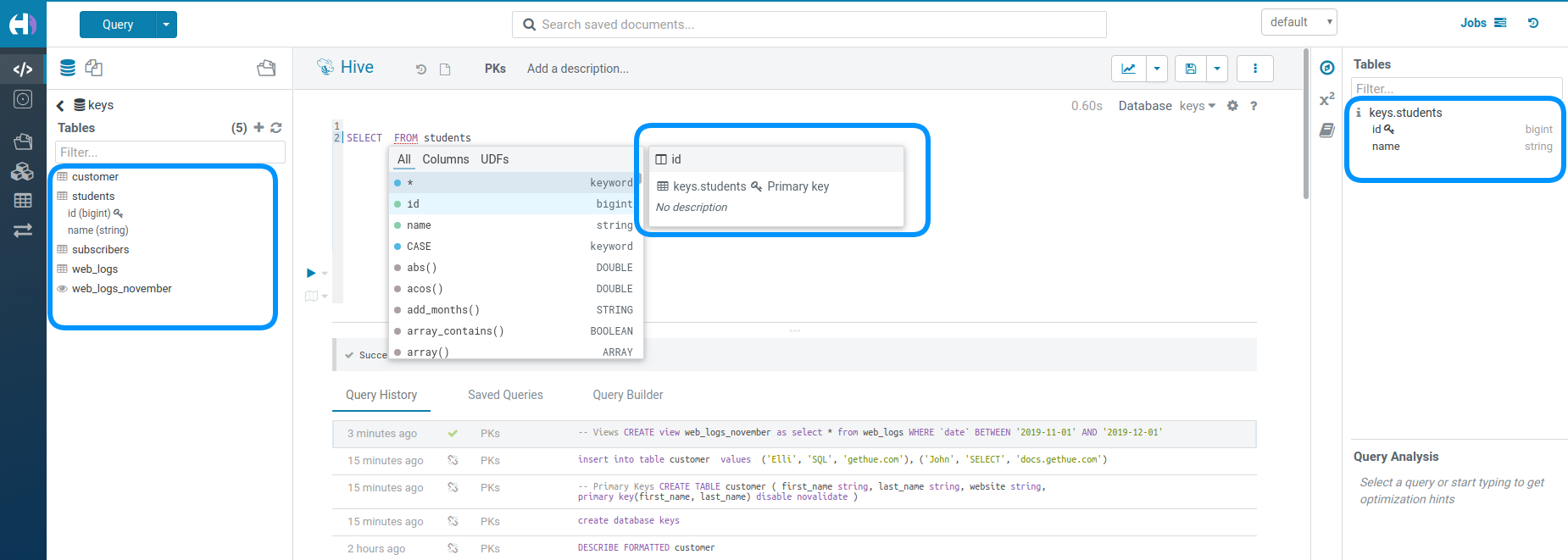
Primary Keys shows up like Partition Keys with the lock icon:
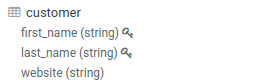
Partitioning of the data is a key concept for optimizing the querying. Those special columns are also shown with a key icon:

Complex or Nested Types are handy for storing associated data close together. The assist lets you expand the tree of columns:

It can be sometimes confusing to not recognize that a table is instead a view. Views are shown with this little eye icon:
![]()
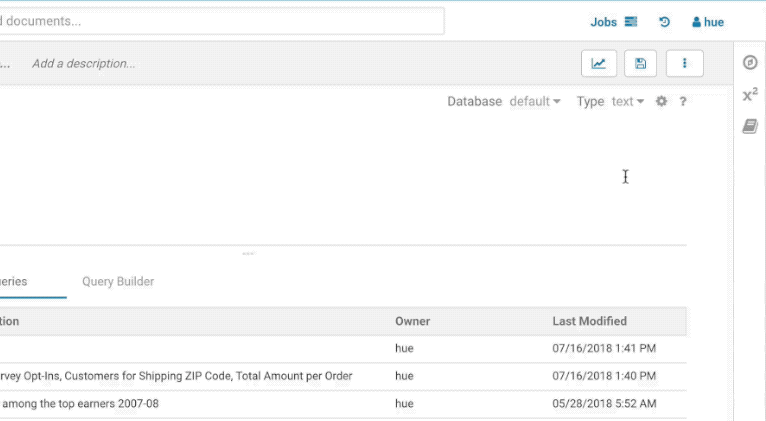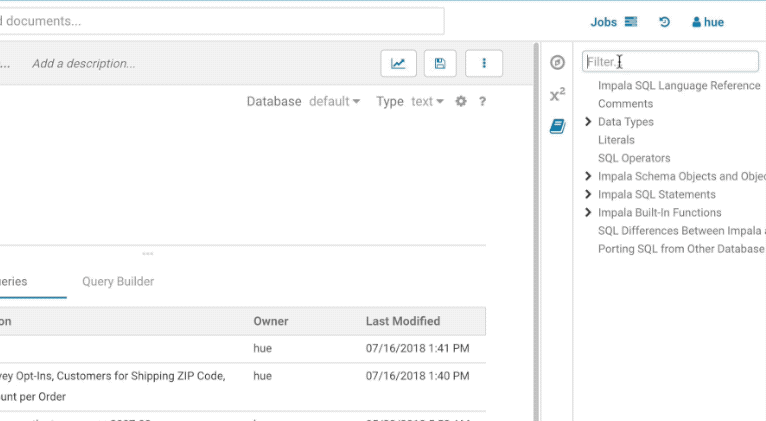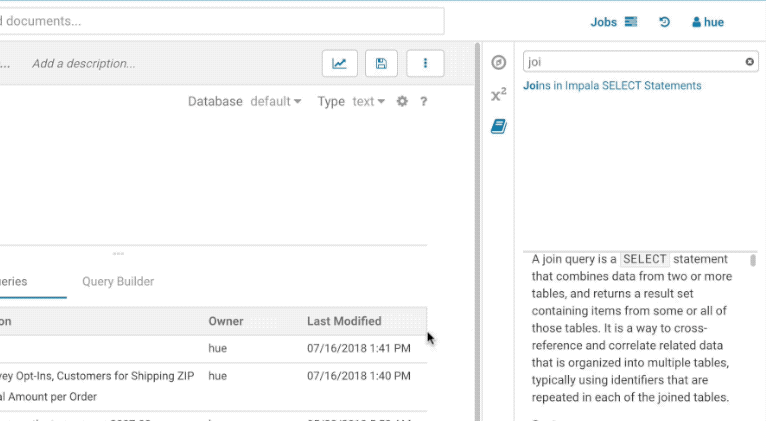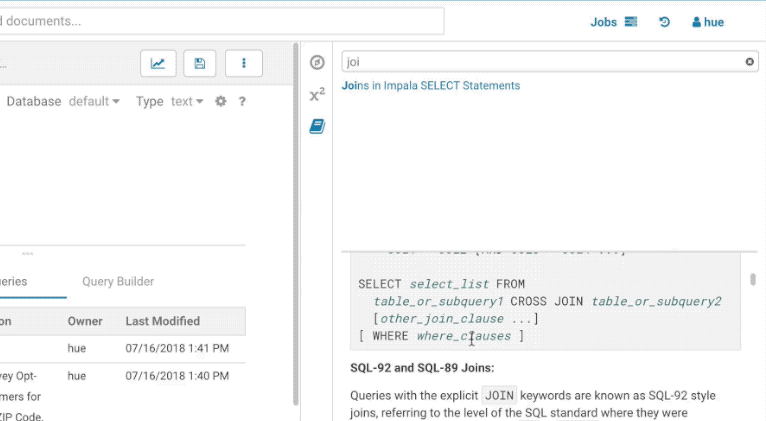
Language reference
You can find the Language Reference in the right assist panel. This assistant content depends on the selected SQL Engines and queries. It will display the current tables, the language and UDFs documentation.
The filter input on top will only filter on the topic titles in this initial version. Below is an example on how to find documentation about joins in select statements.
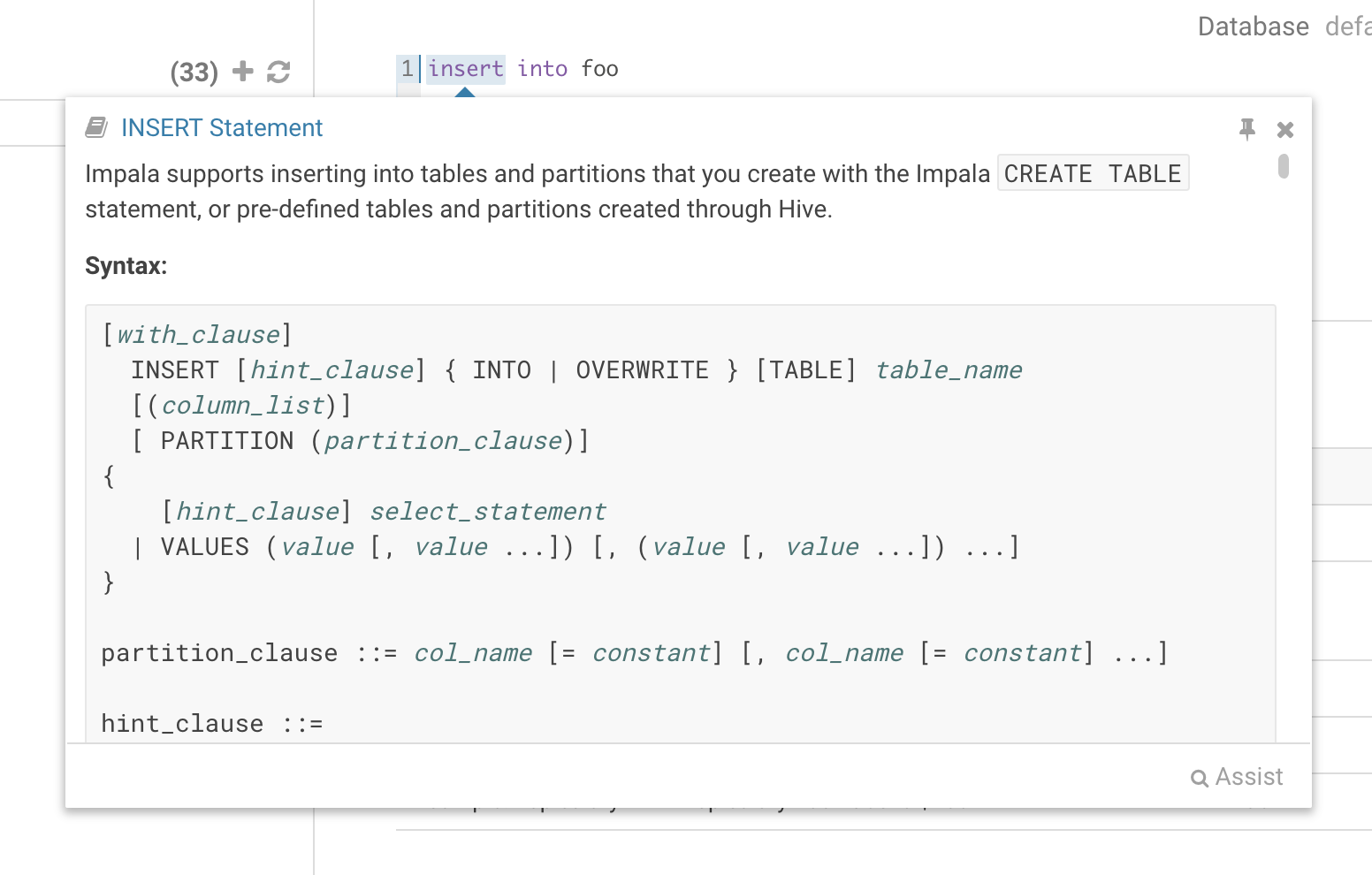
While editing a statement there’s a quicker way to find the language reference for the current statement type, just right-click the first word and the reference appears in a popover below:
Variables
Variables are used to easily configure parameters in a query. They are ideal for saving reports that can be shared or executed repetitively:
Single Valued
SELECT * FROM web_logs WHERE country_code = "${country_code}"
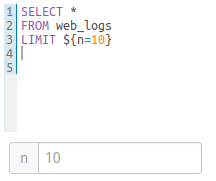
The variable can have a default value
SELECT * FROM web_logs WHERE country_code = "${country_code=US}"
Multi Valued
SELECT * FROM web_logs WHERE country_code = "${country_code=CA, FR, US}"
In addition, the displayed text for multi valued variables can be changed
SELECT * FROM web_logs WHERE country_code = "${country_code=CA(Canada), FR(France), US(United States)}"
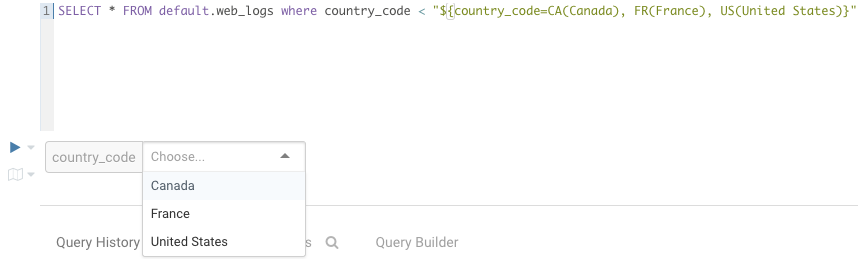
For values that are not textual, omit the quotes.
SELECT * FROM boolean_table WHERE boolean_column = ${boolean_column}
Charting
These visualizations are convenient for plotting chronological data or when subsets of rows have the same attribute: they will be stacked together.
- Pie
- Bar/Line with pivot
- Timeline
- Scattered plot
- Maps (Marker and Gradient)
Modes
Presentation
Turns a list of semi-colon separated queries into an interactive presentation by clicking on the ‘Dashboard’ icon. It is great for doing presentations with a scenario and live results to prove a point or executing reports containing a suite of sequential queries in one click.
Dark
Initially this mode is limited to the actual editor area before extending it to cover all of Hue.
To toggle the dark mode you can either press Ctrl-Alt-T or Command-Option-T on Mac while the editor has focus. Alternatively you can control this through the settings menu which is shown by pressing Ctrl-, or Command-, on Mac.
Query troubleshooting
Pre-query execution
Popular values
The autocompleter will suggest popular tables, columns, filters, joins, group by, order by etc. based on metadata from Navigator Optimizer. A new “Popular” tab has been added to the autocomplete result dropdown which will be shown when there are popular suggestions available.
This is particularly useful for doing joins on unknown datasets or getting the most interesting columns of tables with hundreds of them.
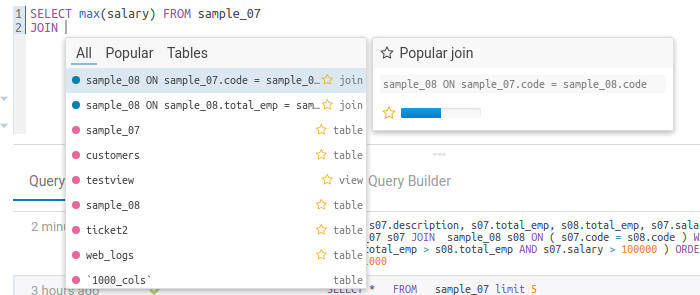
Popular joins suggestion
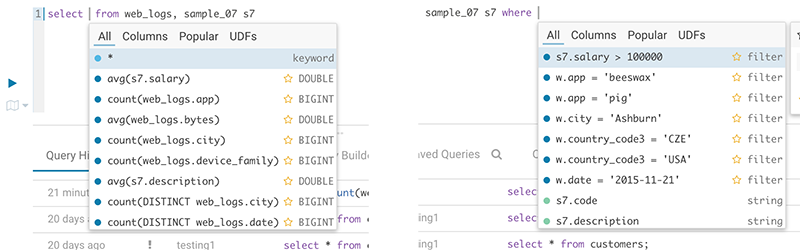
Popular columns and filters suggestion
Risk alerts
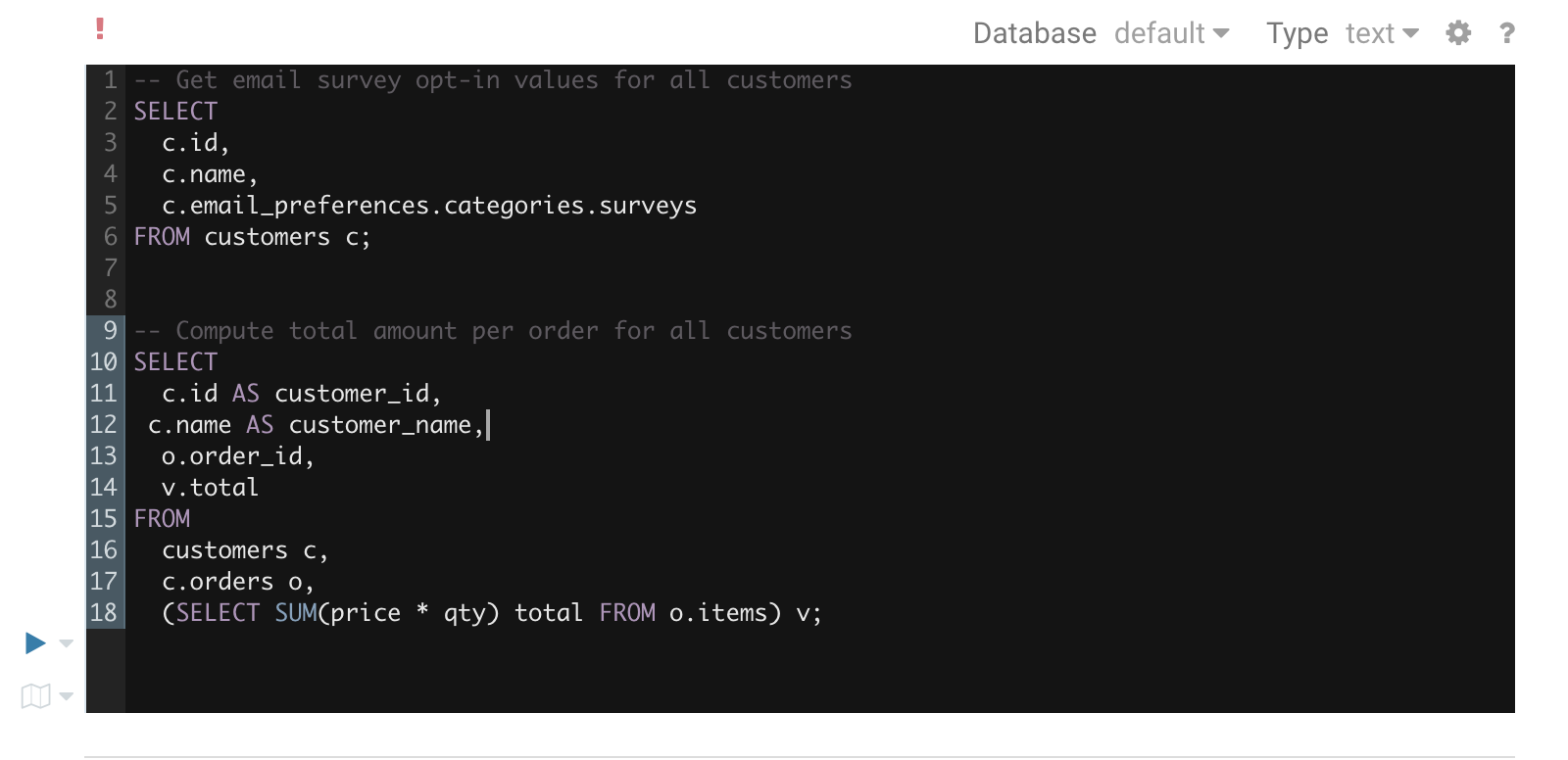
While editing, Hue will run your queries through Navigator Optimizer in the background to identify potential risks that could affect the performance of your query. If a risk is identified an exclamation mark is shown above the query editor and suggestions on how to improve it is displayed in the lower part of the right assistant panel.
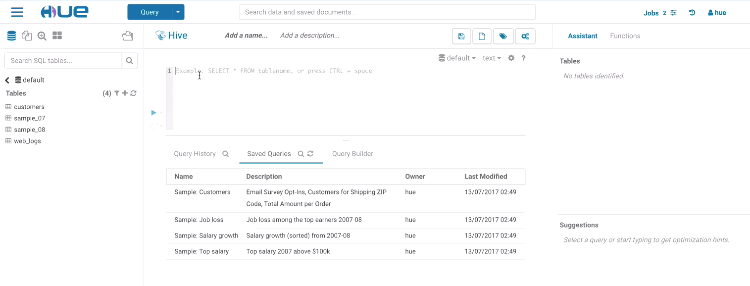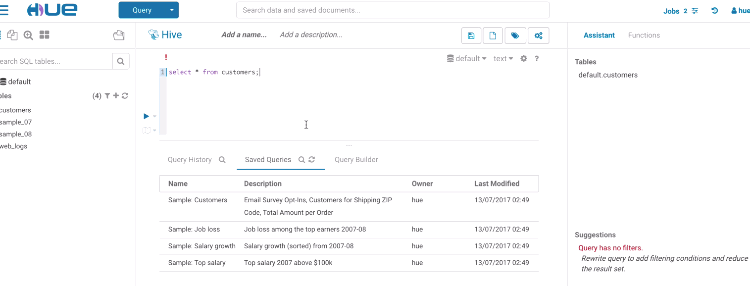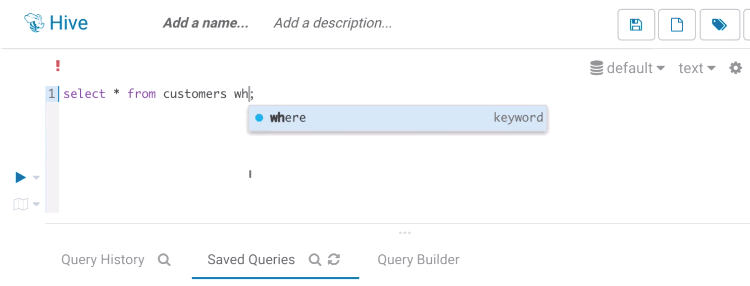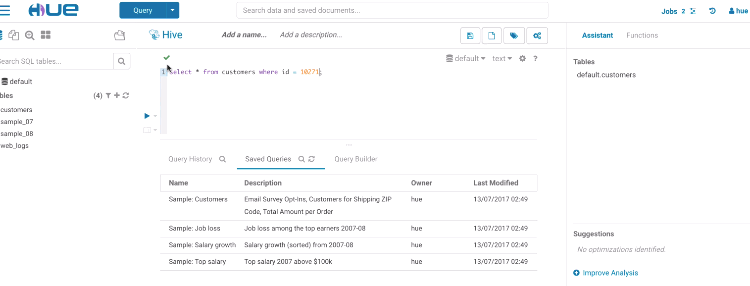
During execution
The Query Browser details the plan of the query and the bottle necks. When detected, “Health” risks are listed with suggestions on how to fix them.
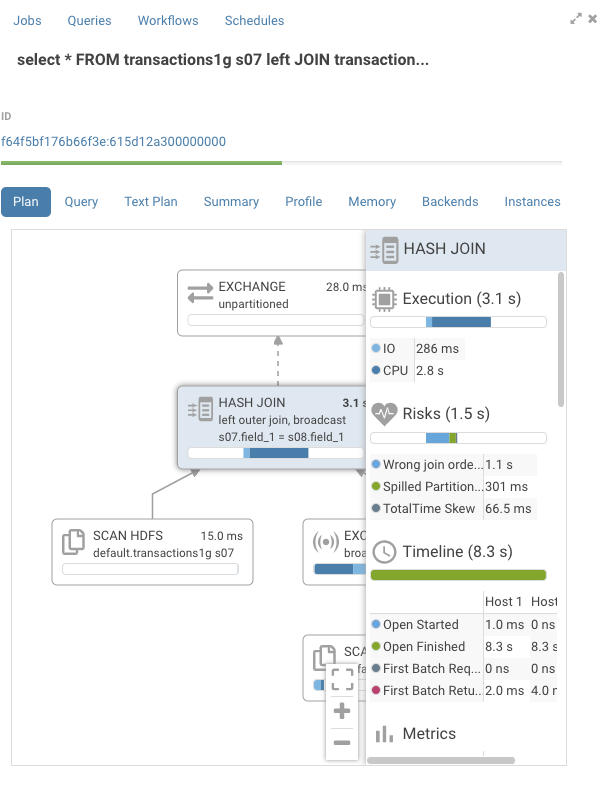
You can find in the documentation a detailed troubleshooting scenario.
Sharing
Similarly to Google Documents, any query can be shared with other users or groups, with read only or edit permissions. Sharing happens on the main page or via the top right menu of the selected application. Shared documents will show-up with a little blue icon.
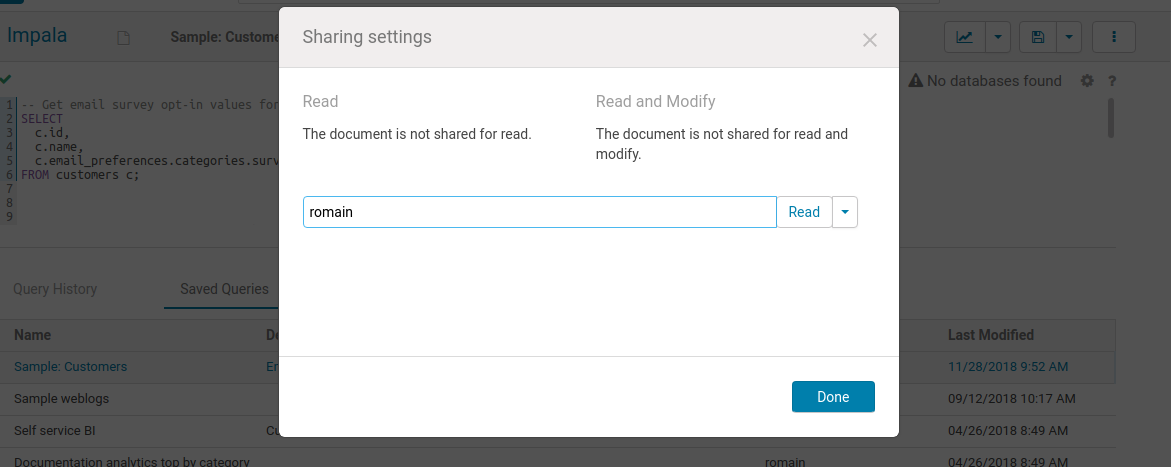
Note: Public links and Gist sharing should be released in the next Hue 4.7!
Next (SQL) steps
Hue 5 and an enhanced SQL Cloud Editor are coming in 2020 for an even more modern Data Query Experience. A Data Warehouse dedicated Hue has also just been released in the Cloudera Cloud Data Warehouse.
Hue is also getting more pluggable with many connectors to the most popular Databases and their dedicated SQL autocomplete.
We will deep dive in greater details on the Cloud capabilities of the SQL Cloud Editor in part three of this series of the 10 years of evolution of Hue. Until then, feel free to comment here or on the Forum and quick start SQL querying!
Romain, from the Hue Team
