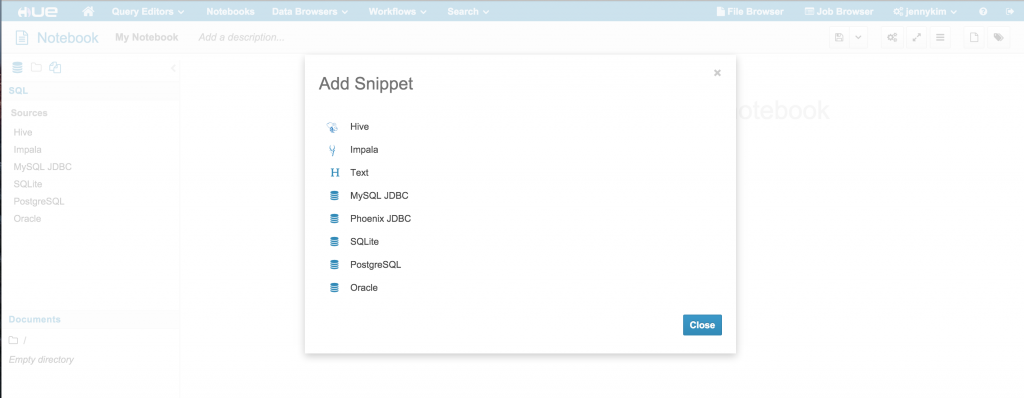
In the latest Hue available in the master branch, we're excited to offer a preview of our entirely revamped and redesigned query editors for Hive and Impala. These query editors will be officially available in the next major Hue 3.10 release.
In this post, we'll demonstrate one of the most powerful features of Hue's new query editor, the ability to integrate it with any JDBC or Django-compatible database!
Integrating PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle and MySQL
Hue's new query editor can easily be configured to work with any database backend that Django supports, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle and SQLite. Some of you may note that these are the same backends supported by Hue's DBQuery app and in fact, adding a new query editor for these databases starts with the same configuration step.
First, in your hue.ini file, you will need to add the relevant database connection information under the librdbms section:
[librdbms]
[[databases]]
[[[postgresql]]]
nice_name=PostgreSQL
name=music
engine=postgresql_psycopg2
port=5432
user=hue
password=hue
options={}
Secondly, we need to add a new interpreter to the notebook app. This will allow the new database type to be registered as a snippet-type in the Notebook app. For query editors that use a Django-compatible database, the name in the brackets should match the database configuration name in the librdbms section (e.g. - postgresql). The interface will be set to rdbms. This tells Hue to use the librdbms driver and corresponding connection information to connect to the database. For example, with the above postgresql connection configuration in the librdbms section, we can add a PostgreSQL interpreter with the following notebook configuration:
[notebook]
[[interpreters]]
[[[postgresql]]]
name=PostgreSQL
interface=rdbms
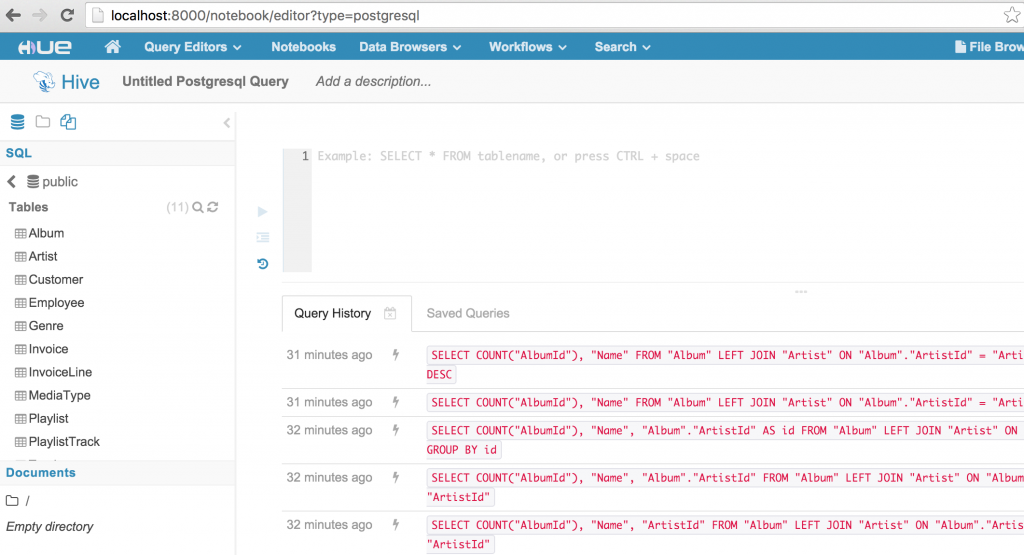
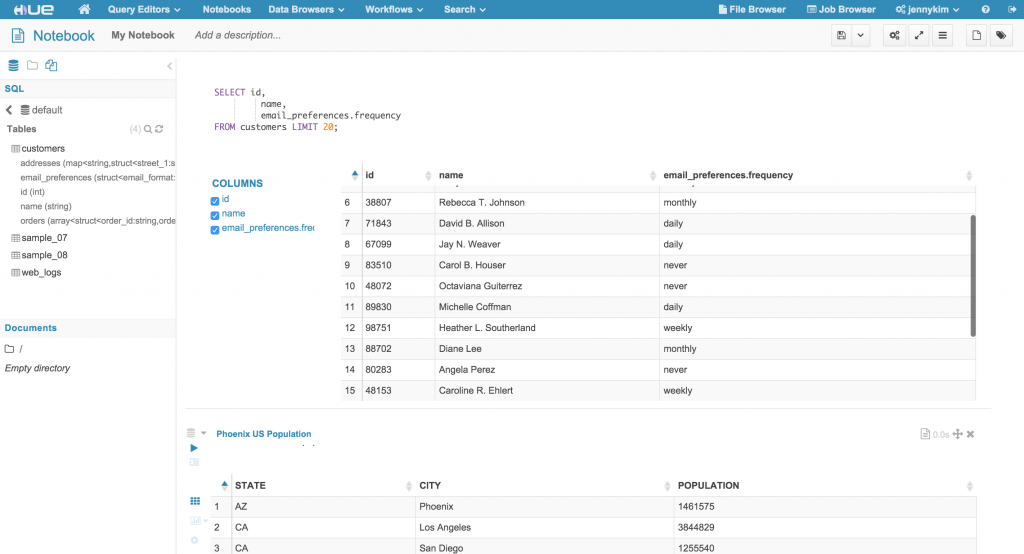
After updating the configuration and restarting Hue, we can access the new PostgreSQL interpreter in the Notebook app:
Alternatively, we can bring up a PostgreSQL query editor by navigating to the URL path /notebook/editor?type=postgresql where the type query parameter is equal to the interpreter name we added in our configuration:
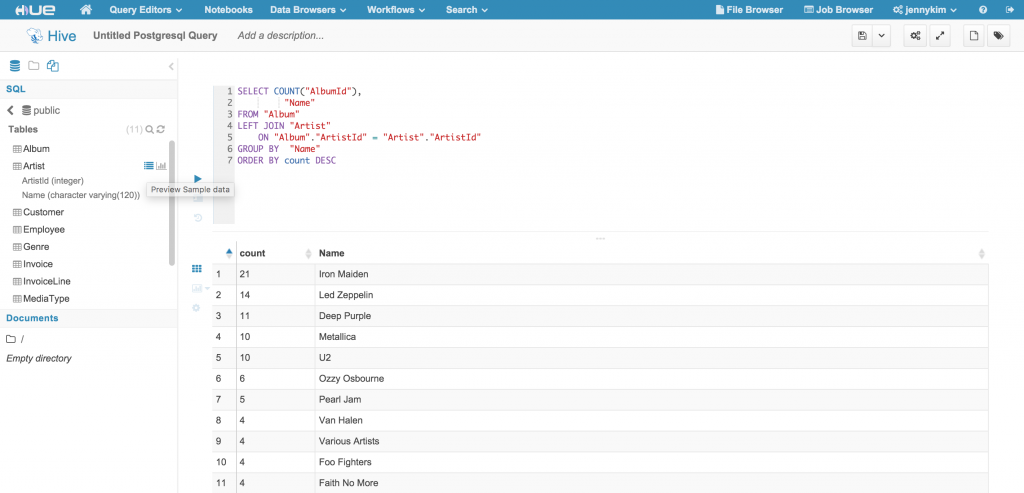
Notice that the left Assist panel has been update to reflect the “Postgresql SQL” data source, and the Databases list should display the available databases based on the configured connection. For interpreters that use the “rdbms” interface, the Assist panel supports drill-down on datasources, databases, tables, and columns, as well as fetching sample data for a given table or column.
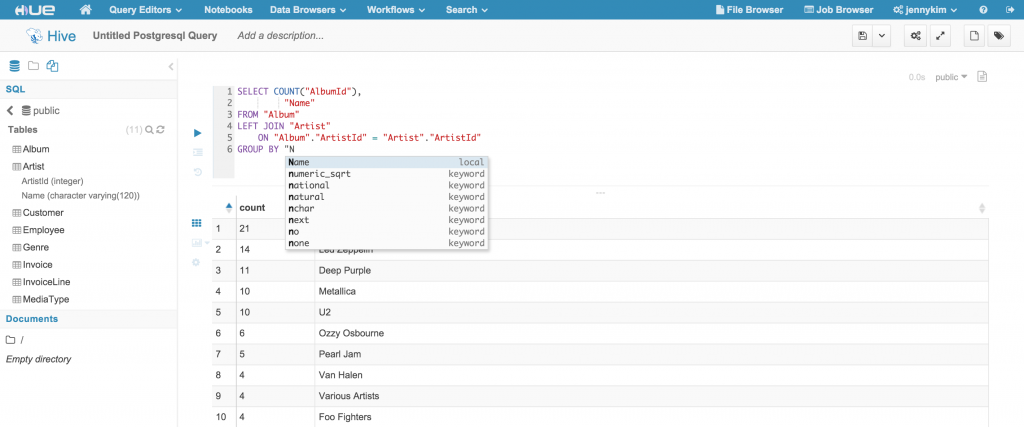
Additionally, the editor supports autocomplete functions that will suggest available database, table and column names as well as query syntax.
Integrating JDBC-compatible databases
The “rdbms” interface works great for MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and Oracle, but for other JDBC-compatible databases Hue now finally supports a “jdbc” interface to integrate such databases with the new query editor!
Integrating an external JDBC database involves a 3-step process:
- Download the compatible client driver JAR file for your specific OS and database. Usually you can find the driver files from the official database vendor site; for example, the MySQL JDBC connector for Mac OSX can be found here: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/. (NOTE: In the case of MySQL, the JDBC driver is platform independent, but some drivers are specific to certain OSes and versions so be sure to verify compatibility.)
- Add the path to the driver JAR file to your Java CLASSPATH. Here, we set the CLASSPATH environment variable in our `.bash_profile` script.
# MySQL
export MYSQL_HOME=/Users/hue/Dev/mysql
export CLASSPATH=$MYSQL_HOME/mysql-connector-java-5.1.38-bin.jar:$CLASSPATH
</code></pre>
- Add a new interpreter to the notebook app and supply the “name”, set “interface” to
jdbc, and set “options” to a JSON object that contains the JDBC connection information. For example, we can connect a local MySQL database named “hue” running on `localhost` and port `8080` via JDBC with the following configuration:[notebook]
[[interpreters]]
[[[mysql]]]
name=MySQL JDBC
interface=jdbc
options='{"url": "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hue", "driver": "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver", "user": "root", "password": ""}'
</code></pre>
TIP: Testing JDBC Configurations
???? Before adding your interpreter's JDBC configurations to hue.ini, verify that the JDBC driver and connection settings work in a SQL client like SQuirrel SQL.
TIP: Prompt for JDBC authentication
???? You can leave out the username and password in the JDBC options, and Hue will instead prompt the user for a username and password. This allows administrators to provide access to JDBC sources without granting all Hue users the same access.
After updating the configuration and restarting Hue, we can access the new JDBC-based interpreter in the Notebook app:
TIP: Multiple snippets in a Notebook
???? As you may recall from previous posts, Hue supports multiple snippets with different types in a single Notebook so you can perform exploratory analysis and cross-validate queries across all your data sources in one place.
Alternatively, we can bring it up in the query editor by navigating to the URL path /notebook/editor?type=mysql where the type query parameter is equal to the interpreter name we added in our configuration:
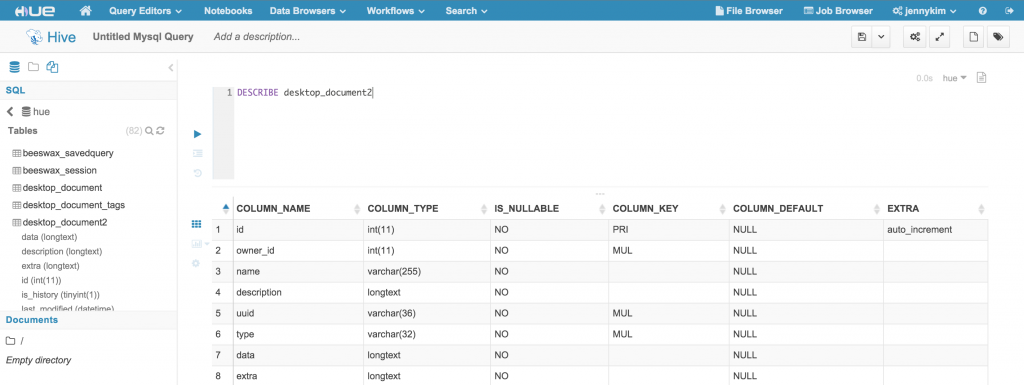
For most ANSI SQL-compliant databases, the Assist panel should display the Data Source, Databases, and a list of Tables and Autocomplete features will be available as well. However, the Assist panel and Autocomplete will not function for databases like Apache Phoenix, which don't support the `SHOW DATABASES` and `SHOW TABLES` syntax.
NOTE: JDBC interface 1000 record limitation
❗️ Currently the JDBC interface does not support pagination of results. As such, Hue limits the result sets from JDBC data sources to 1000 records. We are working on lifting this restriction in an upcoming release.
Of course with both RDBMS and JDBC interfaces, you also get Hue's built-in editor features to auto-format your queries, save queries, view your query history, and visualize/graph your results. We will continue to roll out further improvements and features to the query editor, to provide the best and most flexible yet powerful SQL on Hadoop experience bar none.
Driver URLs and Sample Configurations
We've provided links to JDBC client drivers and sample configurations for some of the most common JDBC-databases below.
SQLServer
Driver
Microsoft's SQL Server JDBC drivers can be downloaded from the official site: Microsoft JDBC Driver
Sample Configuration
[[[sqlserver]]]
name=SQLServer JDBC
interface=jdbc
options='{"url": "jdbc:microsoft:sqlserver://localhost:1433", "driver": "com.microsoft.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver", "user": "admin": "password": "pass"}'
Vertica
Driver
Vertica's JDBC client drivers can be downloaded here: Vertica JDBC Client Drivers Be sure to download the driver for the right version and OS.
Sample Configuration
[[[vertica]]]
name=Vertica JDBC
interface=jdbc
options='{"url": "jdbc:vertica://localhost:5433/example", "driver": "com.vertica.jdbc.Driver", "user": "admin", "password": "pass"}'
Phoenix
Driver
The Phoenix JDBC client driver is bundled with the Phoenix binary and source release artifacts, which can be downloaded here: Apache Phoenix Downloads Be sure to use the Phoenix client driver that is compatible with your Phoenix server version.
Sample Configuration
[[[phoenix]]]
name=Phoenix JDBC
interface=jdbc
options='{"url": "jdbc:phoenix:localhost:2181/hbase", "driver": "org.apache.phoenix.jdbc.PhoenixDriver", "user": "", "password": ""}'
NOTE: Currently, the Phoenix JDBC connector for Hue only supports read-only operations (SELECT and EXPLAIN statements).
Presto
Driver
The Presto JDBC client driver is maintained by the Presto Team and can be downloaded here: [https://prestodb.io/docs/current/installation/jdbc.html][10]
Sample Configuration
[[[presto]]]
name=Presto JDBC
interface=jdbc
options='{"url": "jdbc:presto://localhost:8080/", "driver": "com.facebook.presto.jdbc.PrestoDriver"}'
Drill
The [Drill JDBC driver][11] can be used.
Sample Configuration
[[[drill]]]
name=Drill JDBC
interface=jdbc
\## Specific options for connecting to the server.
\## The JDBC connectors, e.g. mysql.jar, need to be in the CLASSPATH environment variable.
\## If 'user' and 'password' are omitted, they will be prompted in the UI.
options='{"url": "", "driver": "org.apache.drill.jdbc.Driver", "user": "admin", "password": "admin"}'
Kylin
Driver
The Kylin JDBC client driver is maintained can be downloaded here: http://kylin.apache.org/download/. You can find a comprehensive guide on https://github.com/albertoRamon/Kylin/tree/master/KylinWithHue.
Sample Configuration
[[[kylin]]]
name=kylin JDBC
interface=jdbc
options='{"url": "jdbc:kylin://172.17.0.2:7070/learn_kylin","driver": "org.apache.kylin.jdbc.Driver", "user": "ADMIN", "password": "KYLIN"}'
When HS2, RDBMS, and JDBC Are Not Enough
If the built-in HiveServer2 (Hive, Impala, Spark SQL), RDBMS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQLite), and JDBC interfaces don't meet your needs, you can implement your own connector to the notebook app: Notebook Connectors. Each connector API subclasses the [Base API][12] and must implement the methods defined within; refer to the [JdbcApi][13] or [RdbmsApi][14] for representative examples.
Summary
Hue's new query editors are a huge leap forward in enriching and unifying the SQL experience in Hue. We can't wait for you to try it and look forward to your feedback on the [hue-user][15] list or [@gethue][16]!
[10]: http://Presto JDBC Driver Download [11]: https://docs.datafabric.hpe.com/62/Hue/ConfigureHuewithDrill.html [12]: https://github.com/cloudera/hue/blob/master/desktop/libs/notebook/src/notebook/connectors/base.py [13]: https://github.com/cloudera/hue/blob/master/desktop/libs/notebook/src/notebook/connectors/jdbc.py [14]: https://github.com/cloudera/hue/blob/master/desktop/libs/notebook/src/notebook/connectors/rdbms.py [15]: http://groups.google.com/a/cloudera.org/group/hue-user [16]: https://twitter.com/gethue